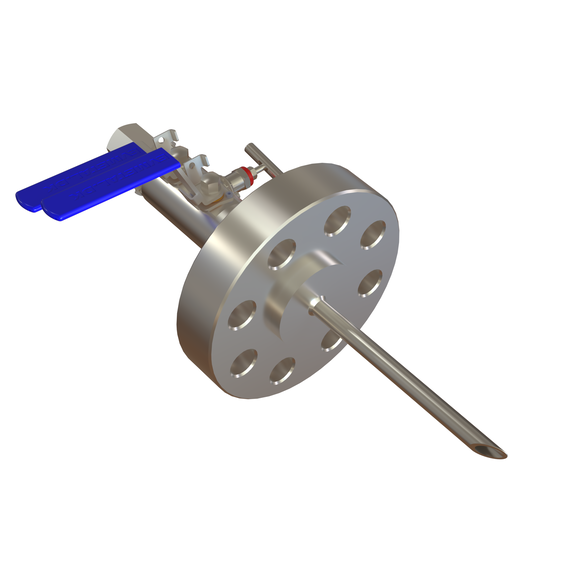
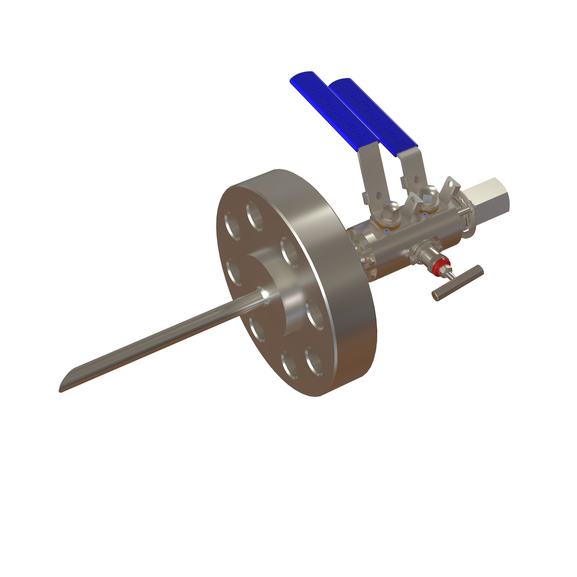
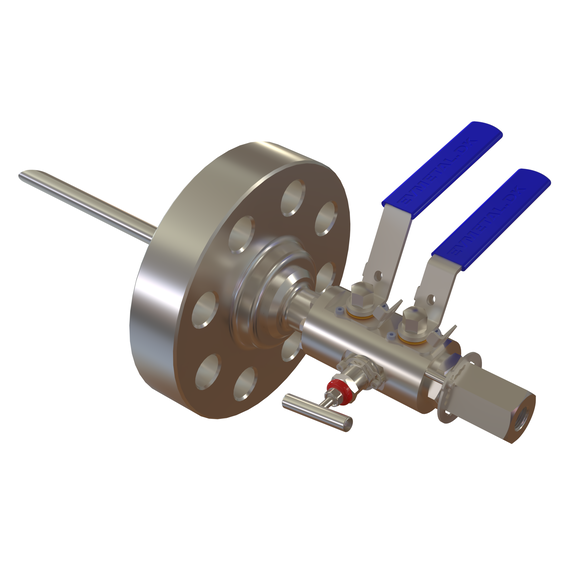
Chemical Injection Quill with integral check valve
Specifications
| Item number: | Quill Stem Material | Flange material | Flange size | Flange Class, ASME B16.5 | Flange face | Quill tip opening | Process Flow Orientation | Quill Length (L) | Quill Shank Diameter |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20Q-3/4#1500 2RTJxNPT | SAF2205 | SAF2205 | 2" | 1500 | RTJ | 45 degr. angle | into 45 degr. | Acc. to customers spec. | 0,75 (Standard) or acc. to customers spec. |
| 20Q-3/4#2500 2RTJxNPT | SAF2205 | SAF2205 | 2" | 2500 | RTJ | 45 degr. angle | into 45 degr. | Acc. to customers spec. | 0,75 (Standard) or acc. to customers spec. |
About the product
Chemical injection quill for offshore oil and gas application
To support clients in their proper planning and technical evaluation, we would like to share some information about a maybe less known product in the industry, the chemical injection quill.
What is a chemical injection quill?
In the oil and gas industry, chemical injection quills are devices used to introduce chemicals at a precise point and rate into a pipeline or vessel, ensuring homogeneous mixing and preventing issues like corrosion, scale formation, and hydrate buildup. These quills are designed to inject chemicals into the center of the flow, promoting even dispersion, and are constructed from chemical-resistant alloys or plastics to withstand harsh conditions. Chemical injection quill is a mechanical device used in the chemical injection process used across many industries. It is an interface equipment between the chemical feed line and the process pipeline. The injected chemicals are controlled to achieve chemical reaction while the quill helps to disperse this into the process pipeline.
Application fields
Chemical injection is used in many application such as injecting additives, chemical/bio treatment, and removal/separation process. To mention a few, below are examples of chemicals used in the oil/gas injection process:
Methanol
Used as hydrate inhibitors. Hydrate solidifies and can cause flow restriction or plugging in wells and flowlines.
Corrosion inhibitor
Used to mitigate the corrosion in wells and pipelines to reduce downtime.
H2S scavenger
Used to treat oil/gas in reducing H2S levels, to reduce health risk and corrosion.
The injection quill could come in various configuration, connections and fittings: From a simple fabricated tube/probe to an integrated assembly with isolation valves and non-return valves. As part of our specialty, we manufacture an integrated chemical injection quill, complete with probe, double block & bleed assembly (2 isolation valves + 1 bleed valve) and an integral non-return/check valve, all in one compact assembly. Looking at the illustration above, this injection quill can also be converted into a sampling quill by a redesign on the probe and without the integral check valve. Sampling quill is used to safely take out fluid samples from the process line for analytical or laboratory purpose.
This type of quill is mounted into the pipeline through a fitting in such a way that the quill/probe is inserted and extends down to the center of the process line. The other end is connected to the chemical feed line by pipe or tubing connections all the way back to the chemical injection skid or chemical Dosing packages that house the pump and chemical tank.
Designing an injection quill
When designing an injection quill following points must be considered:
Wake frequency calculations for the quill: Design calculation (option upon customer request, only)
The wake frequency calculation is based on standard ASME PTC 19.3 TW-2010 for Thermowell since the quill is very similar to it. Since the design requires both thermal and stress considerations, the customer should provide the necessary process data (fluid, temperature, pressure, velocity, flow rate, density, viscosity). If the calculation is not satisfactory, a support collar can also be used to achieve a good result. A poorly designed quill can cause early failures and replacement.
Material
Material grade should be suitable to the service as well as suitability to the type of chemical to be injected. Since the quill is an integrated assembly together with the DBB and check valve, several parameters need to be evaluated as you would do for an isolation valves. This includes the valve body and trim material, whether soft-seat or metal-seat, or other. Mechanical failures are often caused by wrong selection of material grade.
Safe isolation (on customer request, only)
There are quill designs without integral isolation valve or involving only single isolation. To upgrade the safety level, an integral DBB valve is important in certain applications and media. Such is the case for Injection Quill installed in very high pressure API 6A wellheads where pressure is rated at 10,000 psi. Talking about safety, the sealing design and leakage rates of the valve are critical. API PSL 3G PR2 is an option because of very sour gas service.
Dimension
One of the most important parameter in the wake frequency calculation is the length of the quill. The length is usually customized or as specified. In general, the injected chemical is dispersed well if the nozzles are positioned at the center of the pipeline.
Nozzles
The standard for the injection quill is the usual cylindrical tubes or nozzles. However, other applications or users require special designed nozzles for better atomization.
Mounting options
There are different mounting options. To some design, it could be flanged, welded or threaded, but we must make sure that the quill/probe outside diameter (O.D.) will fit all the way down to the process stream. In one experience, the quill/probe outside diameter (O.D.) do not fit because of the welding penetration takes the small tolerances. Also for very high pressure, threaded connection is generally not preferred.
Source: Shahriar_01’S Gigs (Fiverr) & AS-Schneider & Kevin Alamag.
Good to know:
In the oil and gas industry, chemical injection valves accurately deliver precise doses of chemicals—like corrosion inhibitors or demulsifiers—into production systems to prevent issues such as scaling, clogging, and corrosion, thereby ensuring operational integrity, flow assurance, and safety. These specialized valves are integral components of chemical injection systems, controlling the flow of chemicals to prevent equipment failure, improve process efficiency, and maintain hydrocarbon flow from wells.
Purpose of Chemical Injection Valves
Flow Assurance:
They deliver chemicals that prevent build-up in pipes and equipment, keeping oil and gas flowing smoothly.
Corrosion and Scale Inhibition:
Chemicals are injected to prevent corrosion and scaling on the interior surfaces of pipes and wellheads, which can lead to leaks and operational downtime.
Improved Separation:
Chemicals like demulsifiers are injected to help separate water and sediment from crude oil.
Hydrate Prevention:
Inhibitors are used to prevent the formation of gas hydrates, which can clog pipelines.
System Integrity and Safety:
By preventing equipment failure, these valves contribute to the overall safety and reliability of oil and gas operations.
Components of a Chemical Injection System
Chemical Injection Skids:
These are the systems or packages that house pumps, valves, and controllers for the accurate and automated delivery of chemicals.
Chemical Injection Pumps:
These devices, often small and precise, are responsible for the positive displacement and controlled metering of chemicals into the process streams.
Chemical Injection Mandrels:
These are used with the injection valve to deliver chemicals at specific points downhole or on the wellhead, often in corrosive environments.
Chemical Injection Quills:
These are inserted into the flow stream to provide a precise point for chemical dispersal, requiring careful design for stress and thermal considerations.
Chemical Injection Valves:
These control the volume and timing of the chemical injection. Different types are used, including ball valves for reliability and integrated flow controllers for precise metering.
Challenges and Innovations
Inaccurate Dosing:
Traditional systems can struggle with unstable or inaccurate dosing, leading to issues with chemical effectiveness.
High-Pressure Applications:
Many systems must operate under high pressures, requiring robust valve designs and high-performance pumps.
Harsh Environments:
Valves and components must withstand corrosive fluids, high temperatures, and high pressures, demanding specific material selection and design features like double diaphragms to prevent leaks.
Integrated Solutions:
Modern systems are integrating flow metering and control functions into a single unit, like the FluidCom system, for improved accuracy, reliability, and reduced maintenance.
How They Work
Precise Injection:
The quill features a stinger that extends into the pipeline, delivering chemicals directly into the main fluid stream.
Even Dispersion:
By injecting chemicals at the center of the flow, the quill prevents them from being concentrated along the pipe wall, which can lead to inefficient treatment or localized corrosion.
Chemical Resistance:
The body and stinger are made from corrosion-resistant materials like 316 SS or Hastelloy C-276 to handle corrosive chemicals and prevent damage to the pipeline.
Flow Control:
Many quills include check valves to prevent backflow and protect the chemical supply from contamination.
Common Applications in Oil and Gas
Corrosion Inhibition:
Quills inject corrosion inhibitors to extend the lifespan of pipelines and infrastructure.
Scale Control:
They deliver chemicals to prevent scale formation in pipelines and processing systems.
Hydrate Prevention:
Quills are used to inject chemicals that prevent the formation of gas hydrates in cold, high-pressure conditions.
Enhanced Oil Recovery (EOR):
Accurate dosing of chemicals can enhance the process of separating oil from other substances during extraction.
Water Treatment:
Disinfectants are introduced to purify water used in offshore operations or for other processes.
Key Benefits
Improved Efficiency: Ensures proper mixing of chemicals for maximum effectiveness.
Process Control: Allows for precise control of chemical quantities and their point of introduction.
Enhanced Safety: Delivers chemicals safely and accurately, preventing exposure and contamination.
System Integrity: Helps maintain the integrity and efficiency of processing systems.